- News
22 May 2013
Fraunhofer ISE and Soitec achieve 43.6% efficiency with four-junction CPV cell
In an industry project with concentrating photovoltaic (CPV) solar system maker Soitec of Bernin, France, Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE) in Freiburg, Germany is developing a new generation of multi-junction solar cells (for use in CPV power plants) with potential efficiency as high as 50% under concentrated sunlight.
 Picture:
Solar cell wafer with four-junction concentrator cells and test structures. ©Fraunhofer ISE.
Picture:
Solar cell wafer with four-junction concentrator cells and test structures. ©Fraunhofer ISE.
For this, the researchers are replacing the conventional triple-junction III-V solar cell by a new four-junction device. Two dual-junction sub-cell structures are first grown on different III-V compound semiconductor substrates, allowing optimal bandgap combinations tailored to capture a broader range of the solar spectrum (maximizing energy-generating efficiency). Then, using wafer bonding (where the two different semiconductor crystals are compressed together to form covalent bonds at the interface), the sub-cells are fused together so efficiently that the interface promotes current flow through the four-junction solar cell device.
At Fraunhofer ISE, more than 30 individual semiconductor layers had to be engineered and optimized for the new four-junction solar cell. Part of the cell structure was developed at the Helmholtz-Zentrum für Materialien und Energie in Berlin in the research group of professor Thomas Hannappel (now with Technical University Ilmenau) and transferred to Fraunhofer ISE, where it was integrated into the epitaxy process.
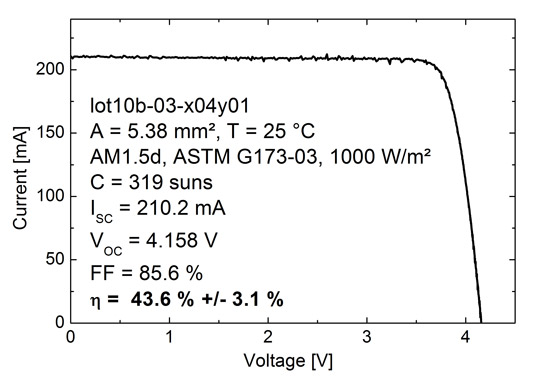
Picture: IV-characteristics of best existing four-junction solar cell under the AM1.5d ASTM G173-03 spectrum at a concentration ration of 319 suns. The measurement was performed at the Fraunhofer ISE CalLab. ©Fraunhofer ISE
The result of the French-German collaboration is a four-junction solar cell device with efficiency of 43.6% at a concentration level of 319 suns, as confirmed by the Fraunhofer ISE Calibration Laboratory. The efficiency remains above 43% in a concentration range of 250-500 suns. It is the first time that such a high efficiency has been obtained for a solar cell with four pn-junctions in series. The further development of this new four-junction solar cell offers the opportunity to improve conversion efficiencies even further to 50% in the future.
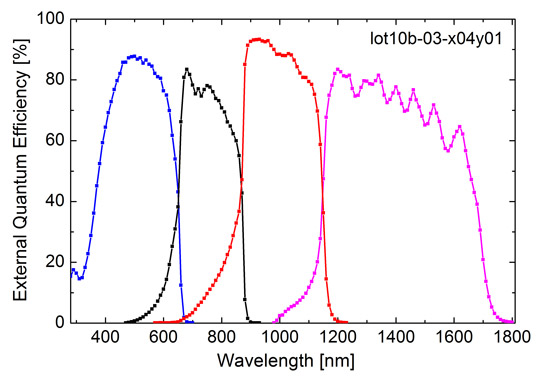
Picture: External quantum efficiency of four-junction solar cell, measured at the Fraunhofer ISE CalLab. ©Fraunhofer ISE.
“For the first time, we can combine the best III-V compound materials in one solar cell device. This leads us into a new generation of multi-junction solar cells showing outstanding efficiency potential,” says Dr Frank Dimroth, department head of III-V Epitaxy and Solar Cells at Fraunhofer ISE. “Now we are able to combine lattice-mismatched crystals which, with conventional technology, cannot be grown on top of each other without deteriorating material quality,” he adds.
Wafer bonding is a key expertise of Soitec and development partner CEA-Leti in Grenoble, France, having been used for decades in manufacturing engineered substrates for the microelectronics industry. Soitec and CEA-Leti together have hence adapted Soitec’s proprietary SmartStacking semiconductor-bonding and SmartCut layer-transfer process technologies to meet the specific requirements of solar cells, namely mechanical stability, optical transparency and electrical conductivity of the bond interface. The process not only enables the stacking of non-lattice-matched materials but also raises the possibility of re-using expensive materials.
The application for the high-efficiency multi-junction solar cells is primarily in Soitec’s CPV modules. In 2009, the firm acquired Fraunhofer ISE spin-off Concentrix Solar GmbH. Since then, Fraunhofer ISE has continued to support Soitec in developing high-efficiency solar cells and point-focus CPV modules. The technology is used worldwide in solar power plants in regions with high solar irradiance.
“Concentrator photovoltaics constantly improves in conversion efficiency and therefore lowers area-related costs,” says Fraunhofer ISE’s director professor Eicke Weber. “The new solar cells, with their new process technology and outstanding efficiency potential, will make an important contribution to the success of concentrator photovoltaics, ” he reckons.
“Boosting efficiency levels is a key step in outperforming the economics of conventional PV,” says Soitec’s CEO André-Jacques Auberton-Hervé. “This great achievement brings strong value to our solar division and validates our strategy and business model in the solar market,” he adds. “This represents a major proof-of-concept, on track to demonstrate a concentrated solar cell with 50% efficiency as soon as 2015.”
The French-German cooperation between Fraunhofer ISE, CEA-Leti and Soitec started with the project ‘SolarBond’ between Fraunhofer ISE and France’s Carnot-Institut, sponsored under the Programme Inter Carnot Fraunhofer (PICF) and funded by the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR) and Germany’s Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) between 2009 and 2011. In this project, the partners demonstrated for the first time the transfer of ultra-thin solar cell layer structures and the application of re-usable engineered substrates (a key milestone on the way to commercializing the new four-junction solar cell). The achievements were honored by the Franco-German Business Award in 2011.
Fraunhofer and CEA-LETI researchers receive Franco-German Business Award
Fraunhofer ISE raises multi-junction solar cell efficiency record to 41.1%
Fraunhofer ISE Soitec CPV III-V multi-junction solar cells
www.programme.inter.carnot.fraunhofer.org



